 You don't have to be a journalism professor to see that national media coverage of hurricanes and wildfires are different in both style and duration. You see it most dramatically when there are a small number of active fires with large impacts happening at about the same time as a hurricane hitting the US coastline. It's even more acute when an incident like the Camp Fire is responsible for more lives lost and perhaps just as much property damage as a typical hurricane. Or the Woolsey Fire where there are deaths and 200,000 residents evacuated. People wonder why the national media is not sending their top anchors to report continuously from the fire lines like they do from the beaches during a hurricane.
1 Comment
Soon after the Yarnell Hill Fire, I wrote a paper on my thoughts and experiences. Considering the passage of time and additional assignments, I might change a few things on the periphery but I think the paper stands up well. I did not want to re-write it and I struggled on how to approach this topic for more than a few days. I decided to do a play-by-play of a briefing I gave on the Yarnell Hill Fire. I post this not to call attention to my being there, but because it was a tough briefing and unlike with other briefings out there, I can tell you what I was thinking and feeling as I analyze the questions and answers. (As I noted in Part 1, I would not have been able to do this without the experiences on Wallow and Rodeo-Chedeski.)
I believe this was the Wednesday after the Sunday fatalities and it is the day the Granite Mountain crew buggies were to be returned to their home in Prescott. The media is congregated at a roadblock on the side of the highway leading into Peoples Valley and Yarnell. The plan was for the crew buggies to leave the fire area and pass by us around 10:00, after which I would brief the media. However, there were delays and when the video starts, it is after 11:00 with no sign of the rigs. By that time, it was hitting 100 degrees and you could tell the media personnel were getting short-tempered after standing by for well over an hour. As a result, they started asking questions without a formal start to the briefing. Also, I never wear a radio for briefings, but had one on here so I could monitor the traffic about the crew buggie transport and planned to take it off as soon as I knew they were headed towards us. So, for perhaps the most difficult briefing in my career, everything was going wrong at the start. 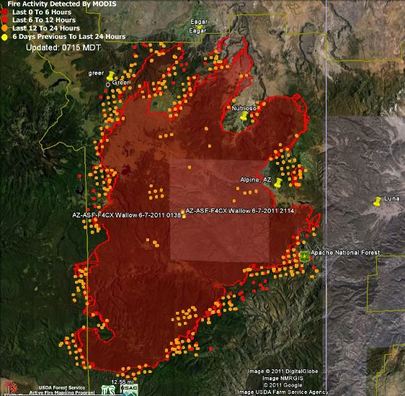 The Wallow Fire started fast and got big faster. On the third day, it went from about 6,700 acres to 40,000 and over the next seven days, it consumed the following acreage:
Upon arriving, I was assigned to lead the Media Group and it was not soon after that it became evident we were not functioning well. Information was too detailed, too fluid, too much, and too frequent for consistency between individual PIOs (and some of those PIOs were, by necessity, forced into roles beyond their capacity). After hearing complaints from both PIOs and media, we held an impromptu press briefing. We then committed to twice-daily briefings and things seemed to settle down a bit for the media, but not for us. What follows are some thoughts on media briefings and large incident issues in general. Much of this post is based off of a piece I wrote soon after leaving the incident, so some of you may have seen that earlier version. As a communicator, it's easy to get wrapped around the axle trying to remember what we can and cannot talk about. For instance, in the wildfire world, I saw a lot of skittishness last year when it came to air tankers--and for good reason. Contracts and such are complicated things beyond most PIO's (and ICs, FMOs, and agency administrators) understanding. When it comes to flying things that weigh a bunch and get politicized easily, it becomes even tougher to not only get it factually correct, but to also navigate through all the potential political potholes.
Yet just because a topic includes complex and controversial issues does not mean we should surrender the whole conversation to others. Media briefings are not something we do every day. Sure, crisis communicators and PIOs often do interviews, but a full-blown live media briefing for a high-visibility incident seldom comes around. I've had the luck--or misfortune--of doing media briefings on four incidents during my career. Some were bigger than others and one was more emotional than the rest, but the common elements are multiple and varied media outlets, live broadcasts, long-term and complex incidents, and regional or national (and international) coverage.
Media briefings are perhaps the most intense thing we can do as PIOs/crisis communicators. Not only are we representing all the responders and speaking to all of the public affected, but because of the high visibility, many others are watching and our reputation--perhaps our career--might be influenced by a single exchange. Because of that dynamic, you can look at media briefings as the most personally stressful communications chore. If you are speaking about fatalities, it amps things up even more. Since the idea of this blog popped into my head, I've been thinking about a post on media briefings. I started writing a few times, but those attempts were ultimately frustrating. As I worked through the process, I came to realize I couldn't build a post around an academic bent or just jot down a basic How-To. No, in order to honestly convey the lessons I learned, it had to be more personal. So please bear with me. As of now, I plan to break the topic up into three posts (maybe four) that will mirror the chronology of my career through the Rodeo-Chedeski, Wallow, and Yarnell Hill fires. (The Eagle Creek Fire will make an occasional guest appearance.) This first one will be the most personal and deal with learning and persevering through failure, the second will cover mostly positive lessons learned, and the third will be about the unique stresses fatalities bring. Every media training I've ever been to advocated doing away with um and uh. However, this principle is based on what is best for media personalities, not crisis communicators. If you read the advice post, you won't be surprised to know I care little about ums and uhs. They are a natural part of speech and can actually lend credibility in a time of crisis. When you use those fillers it is a sign to everyone listening that you are thinking out loud. You are verbalizing your thoughts.
It is a mantra among just about everyone that we must speak with one voice during times of crisis and uncertainty. It is also a mantra among just about everyone that we should speak with one voice during times of certainty and non-crises. One voice is always justified in the name of consistency, to reduce anticipated public confusion, and if we are being honest, it’s done because the larger organization does not trust some folks to get it right when difficult topics come up. Thus, top-down talking points and no deviation from the core message. The problem, as Peter Sandman points out, is that when you speak with one voice, there is a predictable and increased interest in what those other voices might have to say.
|
Occasional thoughts on incident response, crisis communications, wildland fire, and other topics.
Docendo disco, scribendo cogito. Blog DOB: 4/26/2018Copyright © Jim Whittington, 2019. Archives
August 2019
Categories
All
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed